Historical TSWV Predictions: Using the Tobacco Thrips Flight and TSWV Intensity Predictor
go.ncsu.edu/readext?1069313
en Español / em Português
El inglés es el idioma de control de esta página. En la medida en que haya algún conflicto entre la traducción al inglés y la traducción, el inglés prevalece.
Al hacer clic en el enlace de traducción se activa un servicio de traducción gratuito para convertir la página al español. Al igual que con cualquier traducción por Internet, la conversión no es sensible al contexto y puede que no traduzca el texto en su significado original. NC State Extension no garantiza la exactitud del texto traducido. Por favor, tenga en cuenta que algunas aplicaciones y/o servicios pueden no funcionar como se espera cuando se traducen.
Português
Inglês é o idioma de controle desta página. Na medida que haja algum conflito entre o texto original em Inglês e a tradução, o Inglês prevalece.
Ao clicar no link de tradução, um serviço gratuito de tradução será ativado para converter a página para o Português. Como em qualquer tradução pela internet, a conversão não é sensivel ao contexto e pode não ocorrer a tradução para o significado orginal. O serviço de Extensão da Carolina do Norte (NC State Extension) não garante a exatidão do texto traduzido. Por favor, observe que algumas funções ou serviços podem não funcionar como esperado após a tradução.
English
English is the controlling language of this page. To the extent there is any conflict between the English text and the translation, English controls.
Clicking on the translation link activates a free translation service to convert the page to Spanish. As with any Internet translation, the conversion is not context-sensitive and may not translate the text to its original meaning. NC State Extension does not guarantee the accuracy of the translated text. Please note that some applications and/or services may not function as expected when translated.
Collapse ▲In order to help growers determine the potential of management practices for TSWV, the Tobacco Thrips Flight and TSWV Intensity Predictor was developed in collaboration with the NC State Climate Office. Because it is the time when growers are thinking about Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus (TSWV) management, here is a step-by-step guide on how to use the Tobacco Thrips Flight and TSWV Intensity Predictor to create Historical TSWV Predictions. A separate publication will include how to create TSWV Risk Assessments: Using the Tobacco Thrips Flight and TSWV Intensity Predictor.
Using historical TSWV predictions serves several important purposes. First, it helps establish a location-specific baseline of TSWV risk based on past weather patterns and user-reported TSWV incidence, allowing the tool to generate adjusted, more accurate forecasts for current conditions. This is particularly important because field-level variation in cultivation practices, such as transplant dates, imidacloprid use, or location, can greatly influence disease outcomes and are not captured by weather data alone.
By viewing and comparing historical predictions, growers and researchers can evaluate how thrips activity and TSWV risk have fluctuated across seasons, identifying trends linked to warmer winters or unusual rainfall patterns. This retrospective insight enables better planning for transplant timing, early intervention with insecticides or plant activators, and proactive risk management. Additionally, comparing historical tool predictions with actual field observations enhances confidence in the model and informs future decision-making.
To create a historical prediction you will need the information outlined and to follow the detailed steps below.
-
Historical TSWV Incidence: Users input the average historical TSWV incidence (as a percentage) for their location. This data serves as a baseline for the tool’s forecasting.
-
Optional Inputs:
-
Anticipated Planting Date: While optional, entering this can provide tailored recommendations.
-
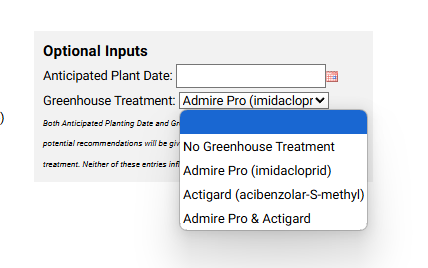
Greenhouse Treatment: Users can specify if they used treatments like Admire Pro® (imidacloprid), Actigard® (acibenzolar-S-methyl), both, or none. These inputs help refine the tool’s recommendations but do not influence the core risk or thrips dispersal estimates.
-
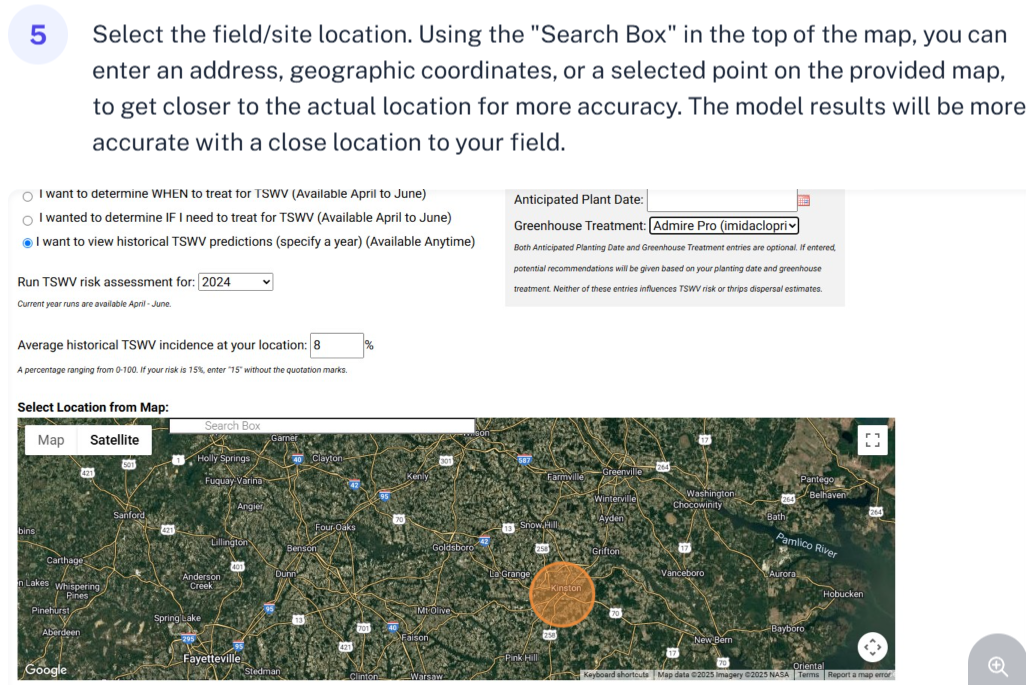
Select the year to view historical TSWV predictions. Year 2024 was selected for this example
Include the average historic TSWV incidence for you site. 8% is the average incidence for the site selected in this example.
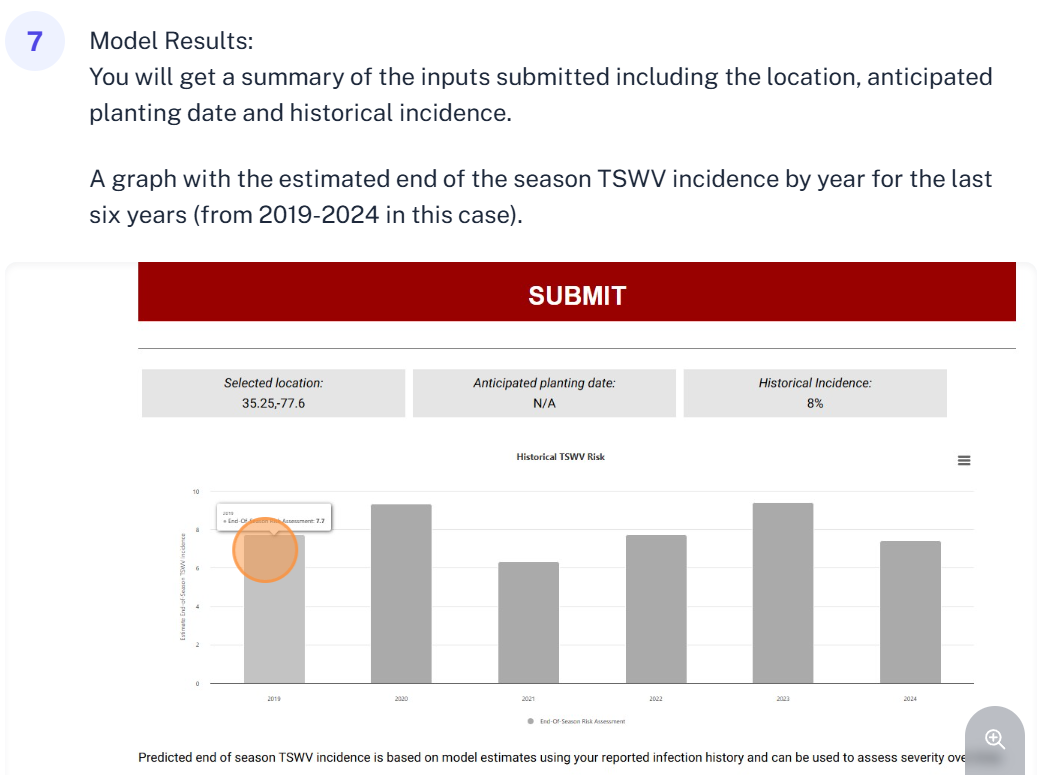
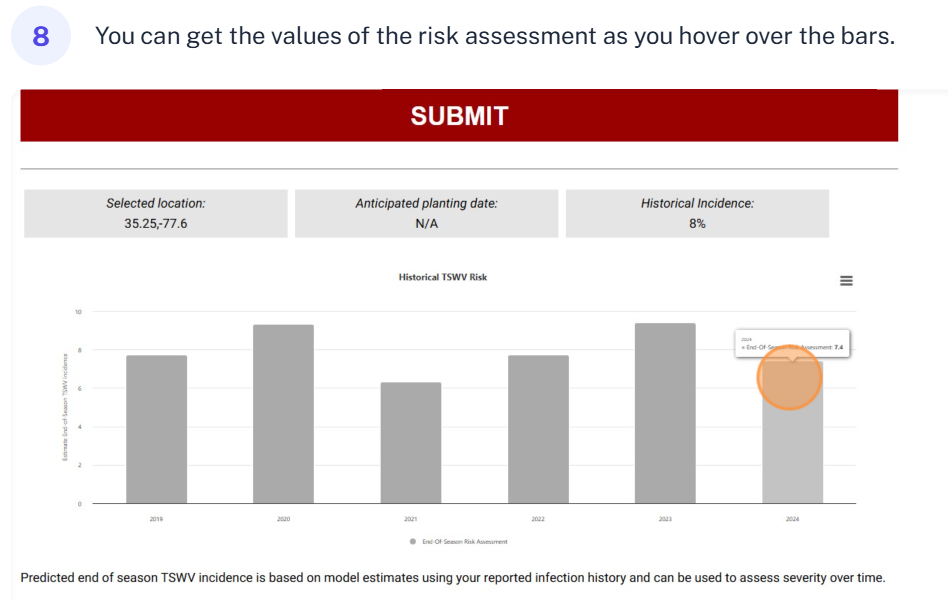
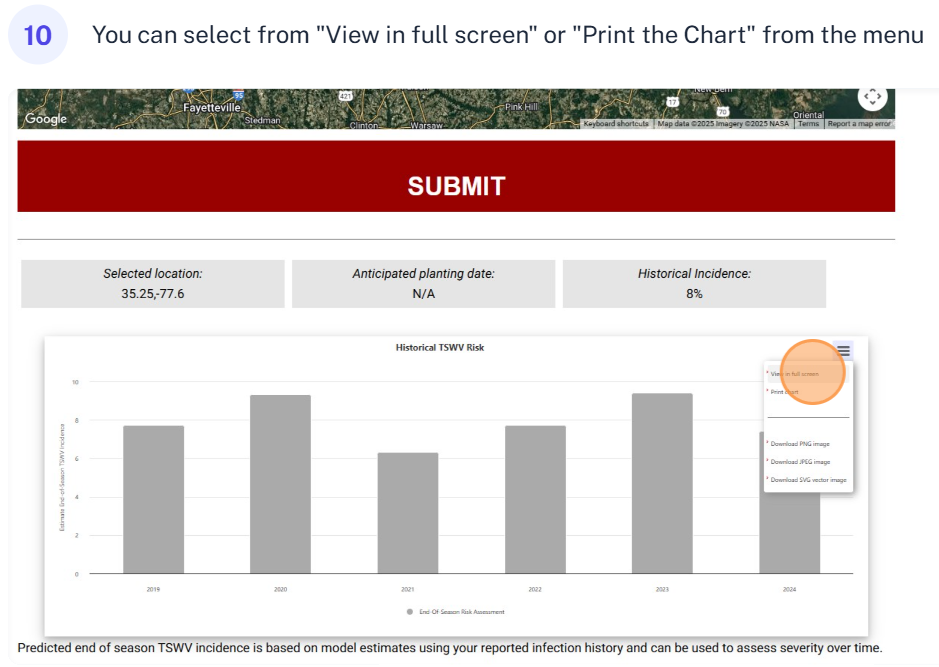
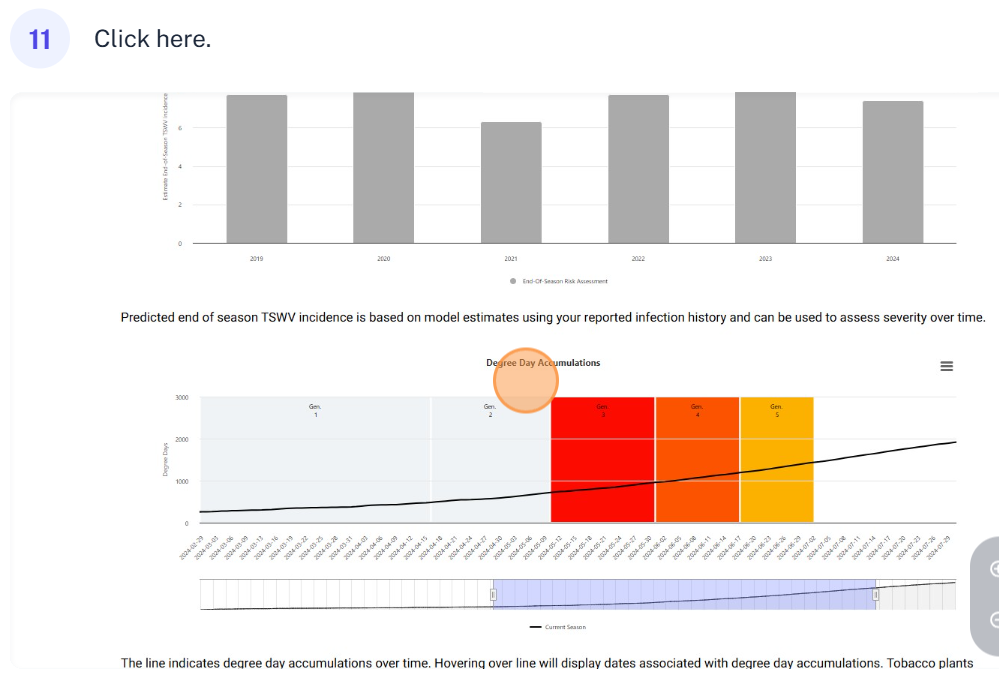
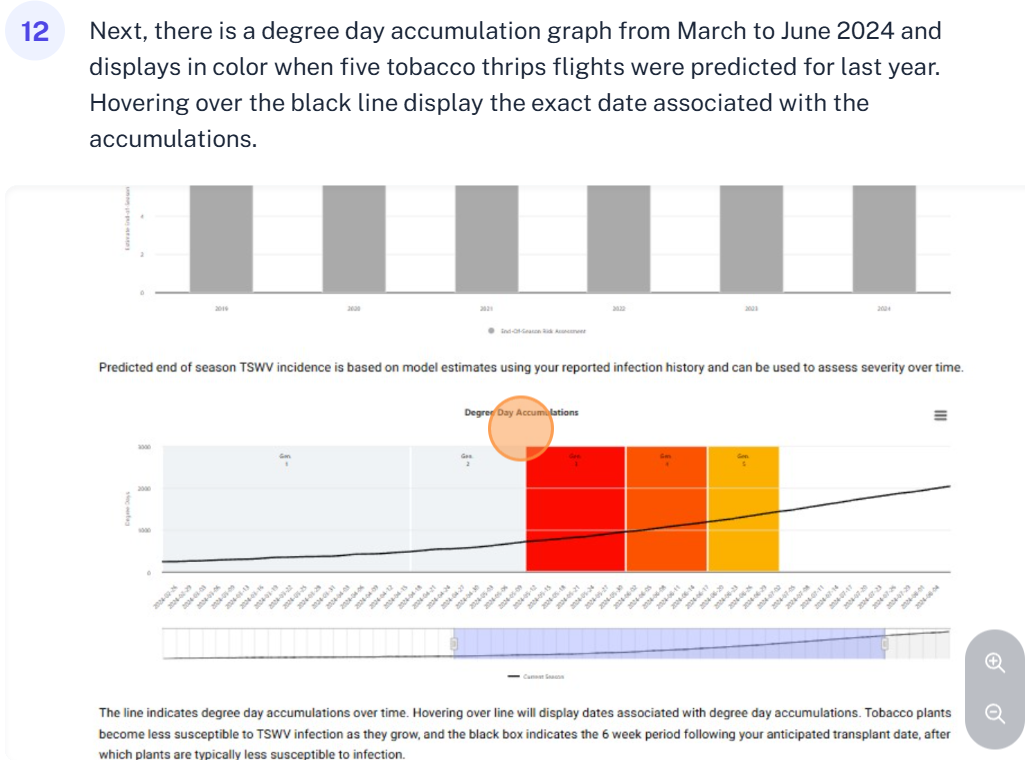
Historical predictions help you see how weather-driven thrips activity and TSWV risk have varied from year to year. This enables growers and researchers to Identify high-risk seasons (e.g., warmer winters, earlier 3rd generation thrips flights), evaluate the consistency or variability of the model, make informed decisions about planting timing, chemical use, or resistance strategies.